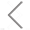Industrial Application of Extracellular Vesicles
Author: Mika Mika Date: May 23, 2022
Industrial Application of Extracellular Vesicles of nanoanalyzer. NanoFCM has widespread application cases in the industrialization of EVs, it can be used in the whole workflow of EV development, from isolation and purification assessment, to EV-based diagnosis/drug delivery, and to the quality control of the final product.
Identification of A Versatile Platform
The engExTM Platform is based on the discovery of two scaffold proteins. Flow cytometry and ELISA were used to measure cellular and EV-associated protein expression, however, these methods fail to determine whether overexpressed scaffold proteins were uniformly distributed among EVs or enriched in subsets. By analyzing EVs at single particle level, the data suggest that overexpression of the candidate scaffolds results in abundant, uniform distribution across EVs.
Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 1729-1743.
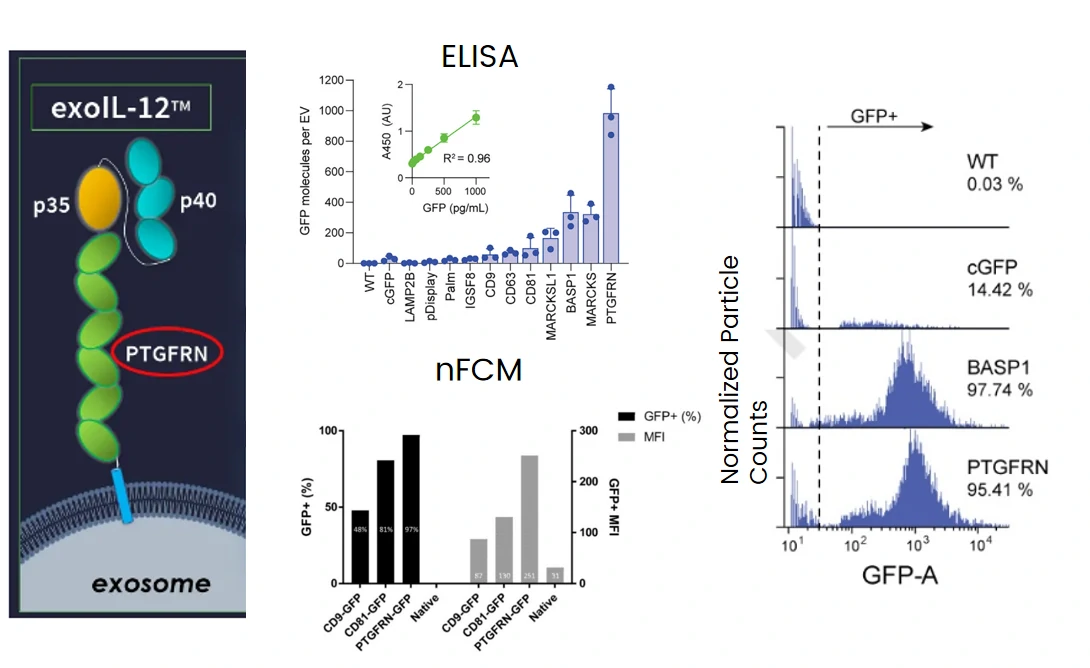
Exosome-Liposome Hybrid Nanoparticles
Thermosensitive liposomes were fused with genetically engineered EVs, the resulting EV-liposome hybrid NPs display CD47 on the surface and bear thermosensitive agents inside. NanoFCM allows the comprehensive analysis of liposomes and exosomes at single particle level, and the evaluation of fusion efficiency.
Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2000515.
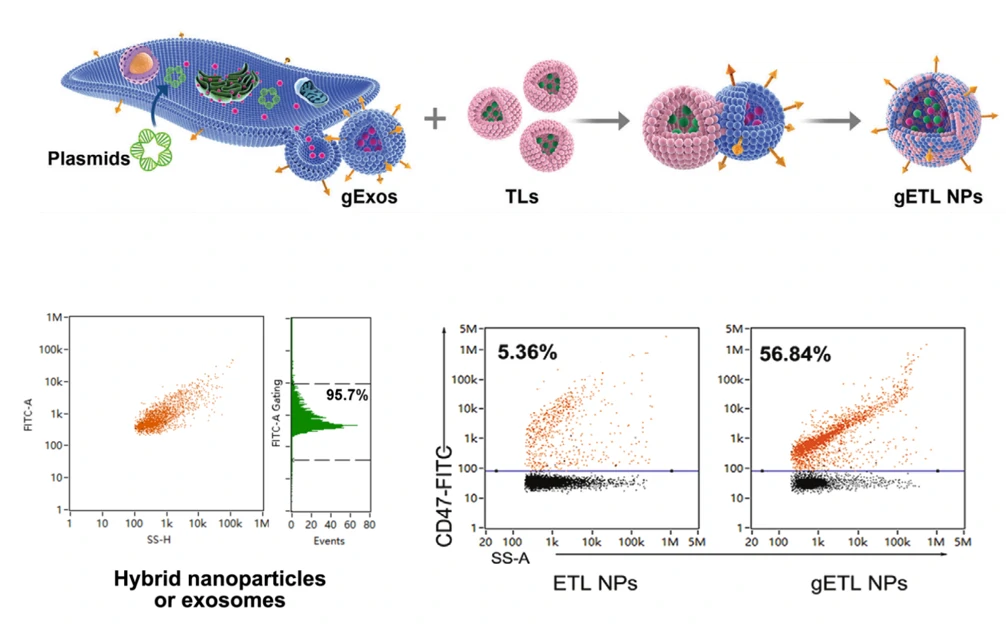
Exogenous Drug Loading
For effective and stable drug encapsulation inside extracellular vesicles, a loading strategy named “Sonication and Extrusion-assisted Active Loading” (SEAL) was developed recently. In the optimization of SEAL, single-particle analysis by NanoFCM was employed to reveal the heterogeneous encapsulation behavior of Dox-EVs and evaluate the loading performance. The as-developed cargo loading approach and NanoFCM-based characterization method will provide an instructive insight in the development of EV-based delivery systems.
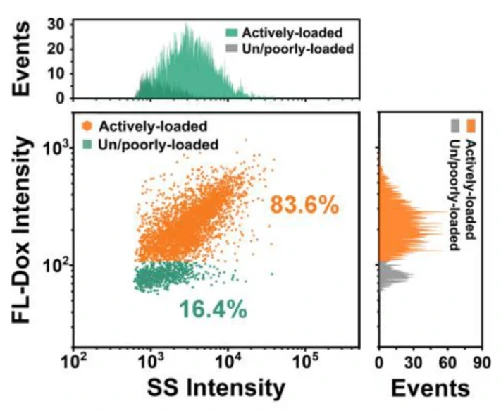
J Extracell Vesicles. 2020;10:e12163.
Nucleic Acids Analysis
It has been demonstrated that EVs carry nucleic acids including RNA and DNA to mediate intercellular communication. Moreover, it is of great importance to understand the behaviour of these nucleic acids in EV-based nucleic acid therapeutics. Upon SYTO 16 staining and enzymatic treatment, the existence forms and distribution of DNA carried by EVs were studied at single particle level.
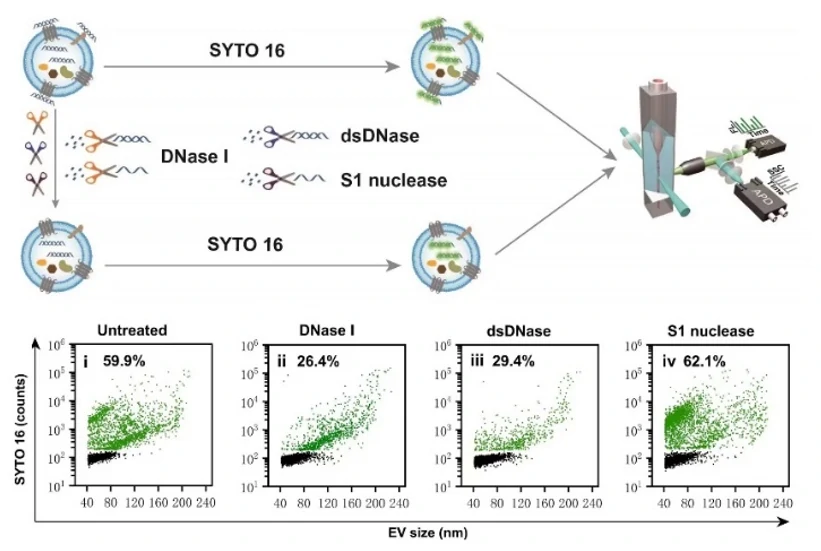
J Extracell Vesicles. 2022;11:e12206
Comparison of Different Isolation Methods
Based on the high-sensitivity and multiparameter analysis features provided by NanoFCM, a new benchmark to the purity and recovery assessment of EVs isolated from plasma, urine, and cell culture was reported. The performance of UC, precipitation and SEC combined with UF, along with a microfluidic tangential flow filtration device, Exodisc were compared comprehensively. Researchers are encouraged to choose the proper isolation method according to the sample type, downstream analysis and their working scenarios.
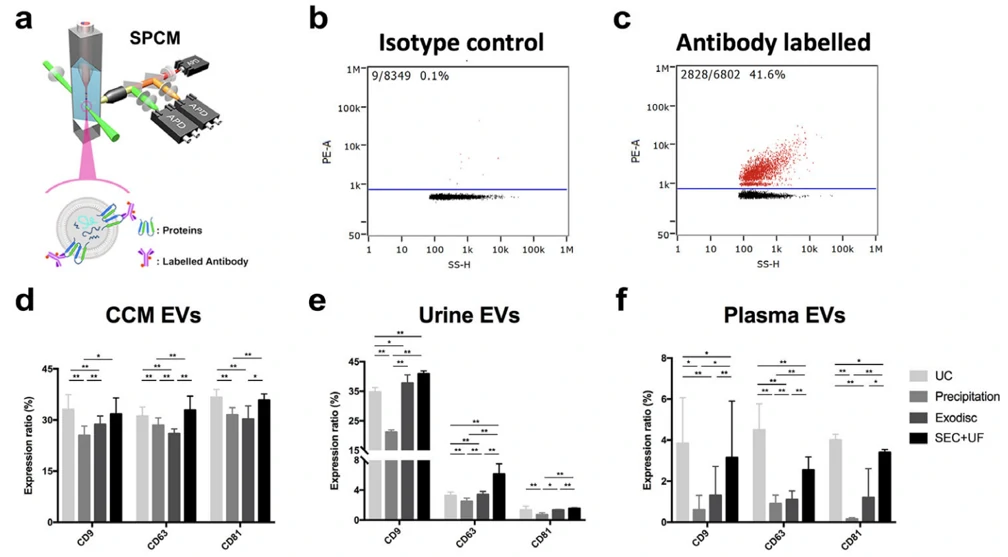
J Extracell Vesicles. 2020;10:e12044.
Early Diagnosis of Cancer
CD147 expression is analyzed quantitatively at the single EV level by NanoFCM. Moreover, NanoFCM allows correlating the protein abundance with vesicle size at the single-particle level, CD147-positive EVs exhibit a range of sizes depending on their cell origin.
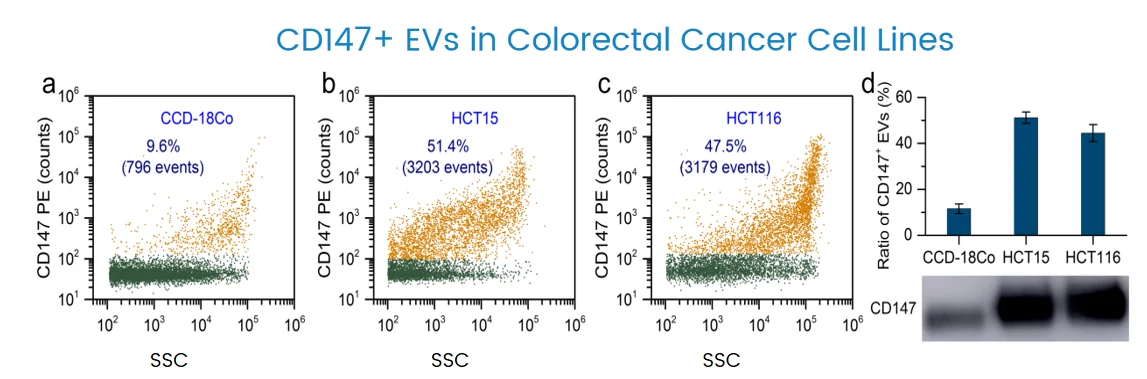
NanoFCM is able to identify the elevated level of CD147 positive EVs for patients at all the cancer stages, even stage I. Moreover, this strategy can be used to track the level of CD147 expression after surgical resection.
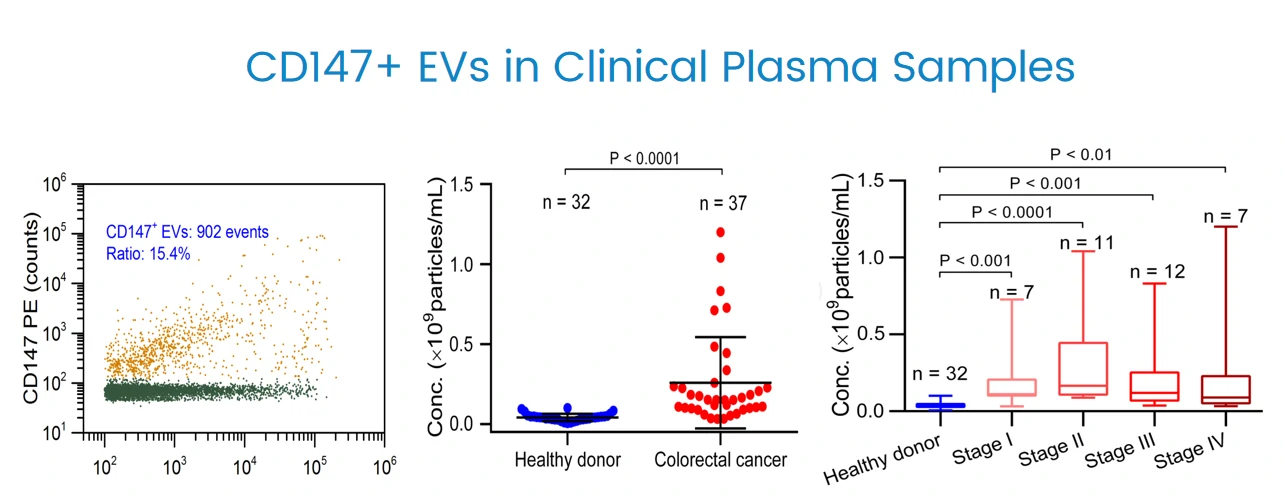
ACS nano, 2018, 12(1): 671-680.
Programmable Modulation for EVs
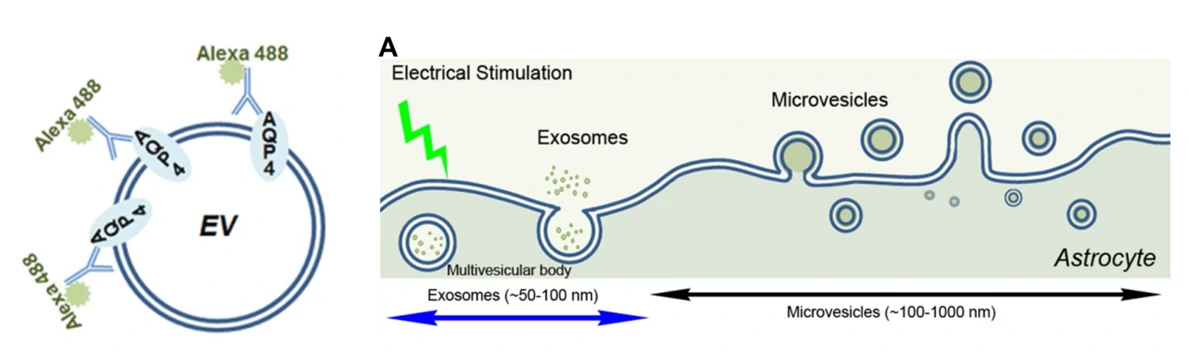
Distributions of EVs after Electrical Stimulation
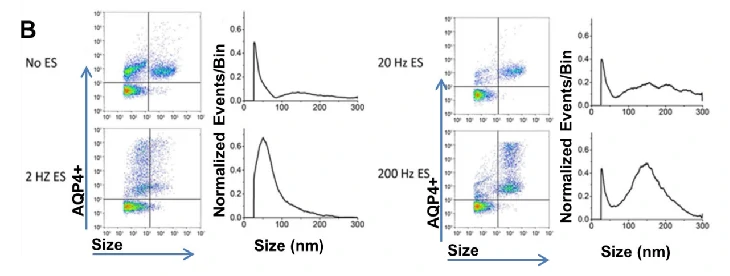
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/566448.
Here is some Industrial Application of Extracellular Vesicles of Nanoanalyzer. Know more about Extracellular Vesicles of Nanofcm, please click here.